FUNCTION
FUNCTION
Process Engine Architecture
Huizheng Workflow Engine is designed on J2EE architecture, It is composed of two kernels, five services and eight interfaces, with process engine and rule engine as its core.
- · "Two kernels":Process engine and rule engine.
- · "Five services":Processing service, rules management service, engine monitoring service, automatic tasking service and messages monitoring service.
- · "Eight interfaces":Process defining interface, management monitor interface, process tasking interface, process applying interface, process interacting interface, access control interface, organization interface and rules invocating interface.
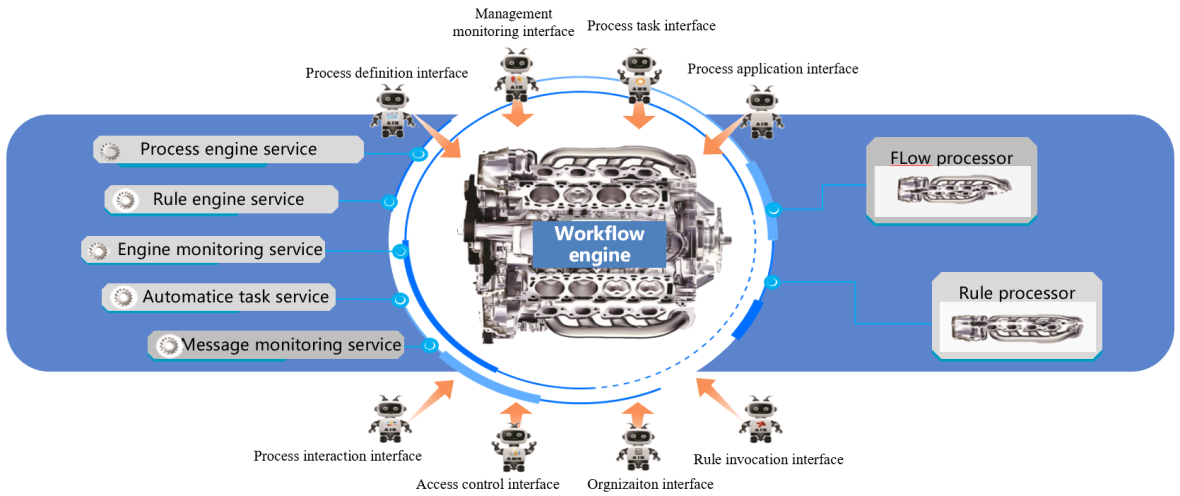
Function Modules
Workflow engine product provide users with a highly flexible, stable, and reliable enterprise-level business process automation and management system architecture, which can fully meet users' various business process management needs.
It mainly includes the following components:
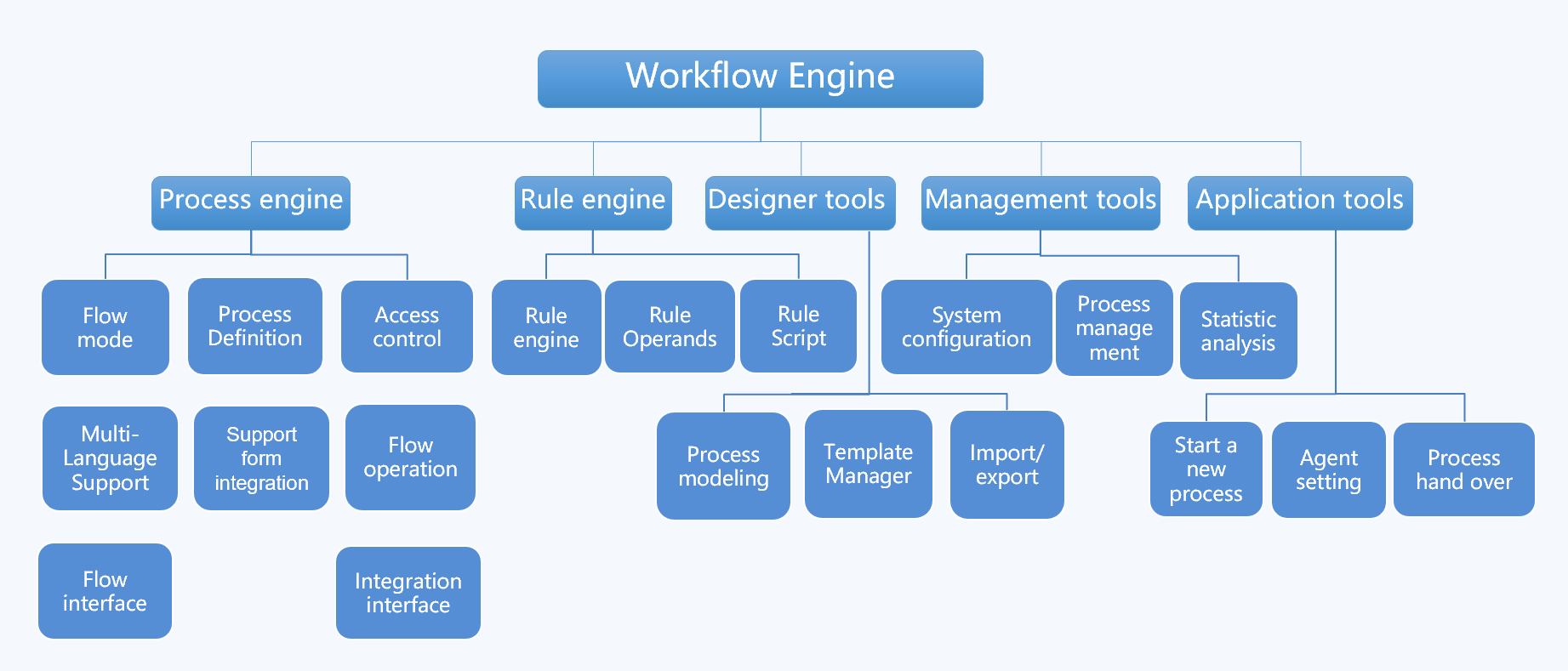
 Workflow Engine
Workflow Engine
Supports up to 42 flow models
Sequential, parallel, synchronous, exclusive selection, simple aggregation, multiple selection, synchronous aggregation, multiple aggregation, discriminator mode, arbitrary loop, implicit termination, multi-instance without synchronization, multi-instance deterministic at design time, multi-instance deterministic at execution time, multi-instance indeterminate at execution time, manual routing, milestone, cancel activity, cancel instance, structured loop, temporary trigger, persistent trigger, region cancel, cancel multi-instance, complete multi-instance task, blocking discriminator, cancel discriminator, partial merge, blocking partial merge, canceling partial merge, overall merge, static multi-instance partial merge, canceling remaining instances after multi-instance partial merge, multi-instance dynamic partial merge, local synchronous merge, normal synchronous merge, linear merge, linear separation, etc.
Task node types
- · Single Operator Activity: the node has only one operator;
- · Multi-Operator: when a node has more than one operator, it will send to all operators at the same time, and the operators can process it by no particular order; (to achieve non-locked multiple concurrent processing, business data preservation conflicts need to be handled by the business implementation itself)
- · Multi-Operator Order:when a node has more than one operator, it will send to the operators in order according to the defined order.
- · Multi-Operator Single:when a node has more than one operator, it will send to all operators at the same time, and as long as one of the operators is processed, the system is submitted to the next node.
- · Manual Merging:various merging rules can be set to merge multiple branches by manual operation.
- · Internal Loop:According to the business logic within the node, implement any number of processing cycles, and only when the conditions are met can the processing be completed.
Event node types
- · Intermediate events:These events are triggered by Process Timing Tasks, immediately executed.
- · Timed events:according to the initiation time and execution cycle parameters set by the process, the flow is triggered at regular intervals.
- · Signal Throwing:the flow automatically call the signal sending API, throwing the signal.
- · Signal Capture:wait for the arrival of signals to match the conditions, and it will automatically trigger the execution of the flow.
- · Message Event:listening to get the message sent by the message-oriented middleware, and after the message parameters matches, it will trigger the execution of the flow.
Node built-in events
- · Node Entry Events: an interface of additional event which will be executed before process enters the node.
- · Node Leave Event: an interface of additional event which will be executed after process leaves the node.
- · Instance Open Event: an interface of additional event which will be executed after the instance is opened.
- · Operation Completion Event: an interface of additional event which will be executed before the node operation is completed.
Extension rules
- · Entry Rules:set the entry rules of the node and control whether the node is allowed to flow in or not.
- · Leaving Rules:set the leaving rules of the node, and controls whether the flow node allows to leave or not.
- · Activation Rules:four activation methods of node can be set: immediate, timing, signal and message. and when the node is activated, the node operator can receive the to-do message and start processing it.
Exception handling
-
Support the handling of various exceptions, including: process time limit exceeded, node time limit
exceeded, activation failure, event execution failures, and customed extended exception types.
There are two ways to handle expiration: - · Message notification, which can send an exception message notification to the process initiator, administrator, or other specified users when an exception occurs.
- · Execute exception handling, include ignore, skip,pending, terminate, or customized exception handling.
Sub processes
Support starting one or more sub processes. support synchronous and asynchronous flow of sub processes with the main process. support dual-way data transfer between main and sub processes.
Multiple operator configuration methods
- · Support setting process node operators according to departments, groups, positions, and personnel.
- · Support dynamic obtain of process operators from fields of form.
- · Support obtaining process operators from process variable parameters.
- · Support obtaining operators according to the hierarchical relationship of organizational structure.
- · Supporting the obtain of operators by means of rule scripts.
Users relationship of organizational structure
- · Support a variety of built-in user relationship settings, which can automatically locate target operators based on organization structure.
- · Support relationships include:user in the same department, direct department superior, all higher-level superior, direct subordinates, all subordinates, higher-level superior, all superior in higher-level departments (including sub-departments), all superior in higher-level departments (excluding sub-departments), departmental interface personal, higher-level positions, higher-level superior, lower-level positions, lower-level position superior.
- · Support customizing new relationship types.
- · Support primary or secondary operator.
- · Support reader.
- · Support setting process agent and can transfer pending todo list to the agent.
- · Support skipping automatically if the node has none operator.
- · Support skipping the operators automatically who have already processed.
Setting time limits
The processing time limit can be set in accordance with the working days, natural days, select overdue
processing mode.
The system automatically sends reminder messages to the operators whose node that reach the warning time
limit according to the built-in scheduled tasks.
Process permission settings
- · Users can be assigned to different operation privileges according to their different identities, as primary operator, secondary operator,processed,reader, creator, or administrator.
- · Users can be assigned different access rights to the form according to the status of the primary operator, secondary operator,processed, reader, creator, and administrator.
- · Users can be assigned access rights to different fields of the form according to their status as primary operator, secondary operator,processed, reader, creator, or administrator.
- · Node permissions set can be copied to other nodes,to improve configuration efficiency.
- · Each process can has its administrator, each department can independently manage their own processes.
- · User who be assigned global readers of a process has the access right to all instances of the process.
- · User who be assigned readers of a specific node has the access right to instances of the process,when the process just flow to this node.
- · After the end of the process, the reader rights of users to the current instance can be kept, or the reader rights of users to the current instance can be reassigned.
Process action engine supported
- · Submit:Process submit operation.
- · Internal Submit:The process submission operation in internal loop node.
- · Parallel Submit:The process submission operation in Multi-Operator node.
- · Free Submit:When submitting the process, the node operator can first add a virtual node, through which process can be used to submit to any node in this process.
- · Save:Temporarily save the process data.
- · Return:Return to the previous submission node.
- · Return and Submit:Return the process instance to the previous submitted node.
- · Return to Any Node:Return the process instance to any node that the process has already passed through.
- · Internally Return:Return operation within a Multi-Operator Order node.
- · Add operator:Add an operator at the current node, this operation can only be used on a Multi-Operator node.
- · Branch add operator:This operation is suitable for nodes with multiple branches. If a node submits some branches for the first time, other branches can be additionally submitted.
- · Take back:Allow the previous node submitter to take back before the current operator handles the process.
- · Withdraw:The creator of the instance can cancel.
- · Transfer:Transfer the operation of the current node to other user for processing.
- · Urge: Send reminder notification messages to the current opertaors.
- · Add Reviewer:The node operator can add reviewers as needed, the reviewer fills in the comments ,and can only submit them to the operator of the current node. this operation is suitable for “Multi-Operator ”,“Multi-Operator Order” nodes.
- · Pre-add Reviewer:The node operator can add new reviewers before current reviewer as needed, the reviewer fills in the comments ,and can only submit them to the next reviewer of the current node. this operation is suitable for “Multi-Operator Order” nodes.
- · Remove Reviewer:The node operator can reduce reviewers as needed before the reduced reviewer fills in the comments. this operation is suitable for “Multi-Operator”,“Multi-Operator Order” nodes.
- · Claim:When a to-do is sent to a department or group, users under the this department or group will receive the claim message and can perform the claim operation if they need to handle this process.
- · Initiate Multi-Operator:Submit the process to multiple users within a node for Multi-Operator operation.
- · Send to Read:Send a notification to a user for review.
- · Add secondary Operator:Secondary operator can only fill in comments and cannot submit the process to the next node.
- · Secondary submit:The secondary operator submit their opinions to the primary within the node.
- · Read:Confirm that current operator have read the relevant information of this process.
- · Jump: Jump to any processing node within the current process instance.
- · Start sub process:Starts the operation of sub processes.
- · Replace Operator:Replace the operator of the current node.
- · Terminate:Terminate the current process, After termination, process cannot be restored. To-do has been changed to be read.
- · Suspend:Process paused.
- · Pause/Resume:Pause/Resume process instance.
- ·
Close:After opening a process instance, the instance data is uploaded to the memory of the workflow
engine to improve processing speed; After closing the process instance, the workflow engine releases
it from memory.
(All above process operation name can be redefined)
 Rule Engine
Rule Engine
Rule calling interface: Rule calling interface specification for process engine calls.
Code line script editor: Provide a window to programmer for writing scripts directly ,support complex rule operations to be written.
Constant: Provide visual rule script editor with boolean or character string.
Instance: Provide visual rule script editor with instance or node data.
Business data: Provide visual rule script editor with object of business data from form.
Personalized operand: Design new rule operand according to business requirements.
 Design Tools
Design Tools
Process Design Management
- · Process Export:Exporting processes to json files. support for single or batch export.
- · Process Import:Importing processes from json files. support for single or batch export.
- · Process Replication:Support replication of processes.
- · Save new version:Save the modified process as a new version, and the old version can also be preserved.
- · Process definition:Support viewing process configuration files in json format.
- · Open local export file:The process json file exported to the local can be opened for browsing.
- · Open Process Definition History Version:Browse older versions of the process definition.
- · Process Category Management:Add,delete,modify process category.
- · Automated process testing:Initiate a process that automatically runs node by node,check the process if it runs as expected.
- · Process instance Management: List all current process instances, support to recovery version, suspend process, resume process, terminate process, replace operator, delete instances, and update process.
Process Configuration
- · Config process:Nodes are added by dragging and dropping. process editor support straight line, fold line, align, zoom out,zoom in,save as new version, save to local. the flow can be drawn by lane according to business management domains.
- · Config node types:Node types include task, event, and gateway types, and can be extended through script development.
- · Config action types:Action types include Submit, Return,Jump,Transfer,Urge,Claim, Terminate,Suspend,Withdraw,Take back,Add operator,Send to Read,Start sub-processes and can be extended through script development.
- · Configure identity:Operator identity include primary, secondary, processed, administrator, creator, and reader, and can be extended through script development.
- ·
Configure user relationships:User relationships include
1)process initiator, previous node operator, current operator.
2)User in the same department, direct department leaders, all superior leaders, direct subordinates, all subordinates, superior leaders, all user in the higher-level department (including sub departments), all user in the higher-level department (excluding sub departments), department interface user, superior positions, user of superior positions, subordinate positions, user of subordinate positions, and return benchmark operator. - · Configure message types:Message interface include: email, system message,sms,instant message.
- ·
Configure extended options:extended options include.
1)Config operator from external.
2)Select the operator from the settings list.
3)Allow selecting departments, groups, and positions when the operator is empty.
4)Skip this node when the operator is empty.
5)Skip this operator when the operator includes the current user.
6)Skip specified node operator.
7)Effective agency settings take effect.
8)Select user only.
 Management Tools
Management Tools
Statistical Analysis
- · Count by instance status:Count the status of the corresponding process instances by all processes or specified processes, display as list, or graphic.
- · Count by operator:Count by the corresponding process instances by operator.
- · Count by processes:Count the corresponding process instances by the specified process, including the number of instances and the number of operations.
- · Quantity statistics->Popular process:Ranking of processes by the number of instances.
- · Quantity statistics->According to process statistics:Counts the number of created, approved, and closed process instances.
- · Quantity statistics->According to people:Count by the number of creations, approvals and overdue instances related to the selected operator, and count the number of task nodes of approvals and take backs under a certain process for that operator.
- · Overdue Process Statistics:The ranking of processes with the highest number of overdue instances, including node overdue and process overdue.
- · Time consuming statistics->Process time consumption statistics:Count the total time consuming(in hours) and percentage by the selected process, as well as the time consuming and percentage of the task nodes of the individual process.
- · Time consuming statistics->User time consumed statistics:Count the total time consuming (in hours) and percentage by the selected operator, as well as the time consuming and percentage of the task nodes of the individual process by the selected operator.
System Management
Tenant Management: Support creating multi-tenants on the same server. each tenant is a virtual
standalone workflow engine service.
System User Management: Add,delete,modify user information, manage user permissions.
Change password: Change the password of the current user.
Process Management
- · Instance Monitoring:Display the number of process instances created and completed data in Line chart, and display the process instances list in memory.
- · Process Log:Retrieve and query process log information.
- · Sharing process:In addition to using the flow modelling to configure node operators, you can also quickly set node operators, readers, and processing deadlines through the simple process operator configuration method of sharing processes.
- · Work Calendar:Set working day of week,for process deadline judgment and automatic processing.
- · Customize Forms:Register and maintain external forms ,integrate with the process engine to implement business requirements.
System Configuration
- · General configuration:Process engine basic properties configuration.
- · Unified cache configuration:Process engine cache configuration.
- · Authorization Information:Display license configuration information.
 Application Tools
Application Tools
Home Page of the Engine
- · Statistics of process data:Includes: the number of all instances, the number of instances in approval, the number of completed instances, the total time spent by process flow, the overdue probability and the number of withdrawn instances
- · Instance Monitoring:Shows the number of process instances created and completed data as a line graph.
- · Exception monitoring: Show the number of overdue instances, the number of terminations and withdrawals of process instances.
- · Memory Monitoring:Showing various states of process instances in Pie chart.
- · Status Monitoring:Showing various states of process instances in Pie chart.
- · System instance monitoring
- · Memory instance monitoring:Monitoring the process instances currently being used by the application system;
- · Historical instance monitoring:Instances that are currently not in use by of the application system.
Launching a new process
Initiate process from the processes list, or view the processes list.
Todo
- · My to-do list:List of instances waiting for current user to handle.
- · Claiming Todo:Show the list of todo tasks that need to be claimed.
- · To be read:List of instances which current user need to read.
Completed
- · Processed:List of instances that current user has processed.
- · Reviewed:List of instances that current user has read.
- · Readable:List of instances that current user can read, but can not mark as read.
- · Launched:List of instances that current user has initiated.
- · Withdrawed:List of instances that current user has withdrawn after initiation, current user can delete these instances.
Agent Setting
- · Set Agent:Current user designate agent of process, the designated agent will receive the to do message.
- · Agent Process:List of processes that have been delegated as agents.
- · Agent History:History of process lists that have been delegated to agents.
- · Receive agent:List of agency tasks to be received.
- · Agent Management:Administrator can set or cancel agent settings.
Process action engine supported
- ·
Transfer
Process transfer:Hand over designate processes including to-do under these processes.
Todo transfer:Hand over to-do list of current user.
Transfer in process:Instances that are handing over by the current user.
Received List:To-do list that others have agreed to receive.
Rejected List:To-do list that others have rejected to receive. - ·
Receive
To be received:To-do list that are waiting for current user to receive.
Received List:To-do list that current user has agreed to receive.
Rejected List:To-do list that current user has rejected to receive - ·
Management
Transferring List:Manage all to-do list that are handing over.
Transferred List:Manage all to-do list that has been agreed to receive.
Rejected List:Manage all to-do list that has been rejected to receive.